- How to add page numbers to your PDF
- Add text field to PDF
- Append multiple PDF documents
- Bulleted list from XML and XSL
- Merge PDF
- Calculate the height of a paragraph in PDF
- Multipage TIFF to PDF
- Convert TXT to PDF
- Convert XHTML to PDF
- Create PDF in C# - Tall Components - Check out our PDF code samples
- Text formatting
- Generate PDF form from XML
- Generate PDF with local images from XML with Xamarin.iOS
- XhtmlParagraph and TrueType fonts
- Add footer with left and right aligned text on same line
- Read and write meta data from PDF
- Stitch PDF documents
- Use multiple licenses
- What is the resulting fontsize in PDF rich text used in SimpleXhtmlShape
What is the resulting fontsize in PDF for rich text used in a SimpleXhtmlShape
TallPDF supports the SimpleXhtmlShape. This shape accepts PDF rich text as its Text attribute. This PDF rich text is xhtml with a small set of supported elements (body, p, i, b, span). See the PDF reference at page 680 under ‘Rich Text Strings’.
In this rich text, css settings can be used to set the fontsize. The following named fontsizes are supported:
- xx-small
- x-small
- small
- smaller
- medium
- larger
- large
- x-large
- xx-large
This sample shows the translation of these named fontsizes to actual fontsizes when used in PDF. ‘larger’ and ‘smaller’ are relative fontsizes. These are calculated relative to the fontsize setting on the SimpleXhtmlShape.
The sample will create a PDF document with 3 pages. Each page will contain a SimpleXhtmlShape. These shapes will be created with a different fontsize. The text of the shapes will be an xhtml string. It presents a list of font settings and shows the actual fontsize for the various named fontsizes.
The sample proves/shows the mapping of the named fontsizes to the actual fontsizes. It shows:
- Absolute fontsizes are mapped independent of the fontsize of the shape
- Relative fontsizes are mapped relative to the fontsize of the shape
C# code sample with overview of fontsize mapping for named fontsizes used in a SimpleXhtmlShape
Xhtml that will be used
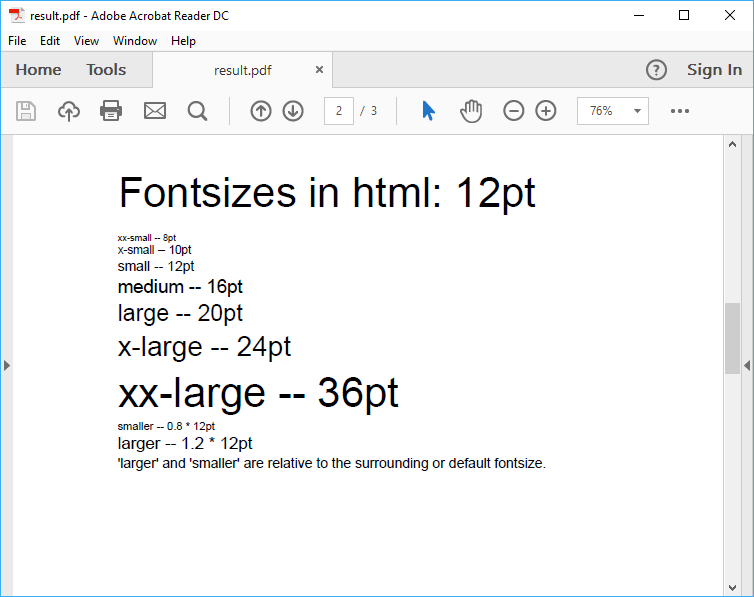
This is the content of the sample file that we use with a fontsize of 8pt. There are also files for fontsize 12pt and 18pt.
<body>
<p style='font-size: xx-large;'>Fontsizes in html: 8pt</p>
<p></p>
<p><span style='font-size: xx-small;'>xx-small</span><span style='font-size: xx-small;'> -- </span><span style='font-size: 8pt;'>8pt</span></p>
<p><span style='font-size: x-small;'>x-small</span><span style='font-size: x-small;'> -- </span><span style='font-size: 10pt;'>10pt</span></p>
<p><span style='font-size: small;'>small</span><span style='font-size: small;'> -- </span><span style='font-size: 12pt;'>12pt</span></p>
<p><span style='font-size: medium;'>medium</span><span style='font-size: medium;'> -- </span><span style='font-size: 16pt;'>16pt</span></p>
<p><span style='font-size: large;'>large</span><span style='font-size: large;'> -- </span><span style='font-size: 20pt;'>20pt</span></p>
<p><span style='font-size: x-large;'>x-large</span><span style='font-size: x-large;'> -- </span><span style='font-size: 24pt;'>24pt</span></p>
<p><span style='font-size: xx-large;'>xx-large</span><span style='font-size: xx-large;'> -- </span><span style='font-size: 36pt;'>36pt</span></p>
<p><span style='font-size: smaller;'>smaller</span><span style='font-size: smaller;'> -- </span><span style='font-size: 6.4pt;'>0.8 * 8pt</span></p>
<p><span style='font-size: larger;'>larger</span><span style='font-size: larger;'> -- </span><span style='font-size: 9.6pt;'>1.2 * 8pt</span></p>
<p>'larger' and 'smaller' are relative to the surrounding or default fontsize.</p>
<p></p>
</body>
In the first column the named fontsize is used to set the fontsize. In the second column the calculated fontsize is used. This allows us to verify that the mapping, as presented in the table, is correct. Both columns in a row should show the same fontsize.
Step 1: Create a SimpleXhtmlShape
The SimpleXhtmlShape uses the Xhtml string that was generated to set the ‘Text’ attribute. The ‘DefaultFontSize’ attribute of the shape is set.
static private void FontSizeMapping(Section section, Int32 fontsize)
{
var filename = $@"..\..\fontsize{fontsize}.html";
Drawing drawing = new Drawing(
section.PageSize.Width - section.Margin.Left - section.Margin.Right,
section.PageSize.Height - section.Margin.Top - section.Margin.Bottom);
section.Paragraphs.Add(drawing);
SimpleXhtmlShape shape = new SimpleXhtmlShape();
shape.Dock = DockStyle.Top;
shape.DefaultFontSize = fontsize;
shape.Text = File.ReadAllText(filename);
shape.Width = drawing.Width;
drawing.Shapes.Add(shape);
}
Step 2: Create the PDF document with 3 shapes with different fontsizes
String fileName = @"..\..\result.pdf";
Document document = new Document();
Section section = document.Sections.Add();
FontSizeMapping(section, 8);
FontSizeMapping(section, 12);
FontSizeMapping(section, 18);
// Writing the PDF document to disk
using (var file = new FileStream(fileName, FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write))
{
document.Write(file);
}
// open the PDF document
Process.Start(fileName);
Creating the fontsize mappings with 3 different fontsizes for the XhtmlShape will show that the relative fontsizes (‘smaller’, ‘larger’) are calculated relative to that fontsize and that absolute fontsizes are calculated independent of the fontsize setting on the shape.