- Add a link to PDF with an external destination
- Add a link with an internal destination to PDF
- Add a note to PDF
- Add barcodes to PDF
- Add bookmarks to PDF
- Add footer to PDF
- Add simple html text to PDF
- Add hyperlink to PDF
- Add Long Term Validation (LTV) data to an existing signature
- Add multiline text to a PDF document
- Add a rubber stamp annotation with a custom icon
- Add single-line text to PDF
- Add Stamp to PDF
- Add tags to existing PDF
- Add text field to PDF
- Add a Diagonal Watermark to PDF in C# - TallComponents - PDF Library
- pdfkit5 - detailed changes to the API - Tall Components
- Append two or more existing PDF files
- Change the color inside a PDF
- Change the formatting of a numeric field
- Change page orientation PDF
- Clip PDF page content in C#
- .NET Core console app on MacOS
- Convert PDF to plain text
- Convert SVG to PDF
- Create a text annotation in PDF with rich text
- Create formfields in PDF documents
- Create a new digitally signed PDF document
- Create rectangles with rounded corners
- Create tagged PDF
- Create text with decorations
- How to create a tiling for shapes in PDF
- Crop content on a PDF page
- Determine the content bounding box
- Determine if a PDF only contains images
- Digitally sign a PDF form in C# or VB.NET
- Disable submit button after submitting
- How to downscale all images in a PDF
- Download and convert image to PDF
- How to downscale all images in a PDF
- Vector graphics in PDF
- Fill XFA form and export XDP data
- Fill and save dynamic XFA form
- Merge XDP data with dynamic XFA form
- Dynamic XFA
- How to embed files in a PDF document
- Embed TrueType font in PDF
- EMF to PDF as vector image
- Export FDF from PDF form
- Extract embedded files from PDF
- Extract glyph boxes from PDF
- Extract glyphs and sort by reading order
- Extract graphics from PDF
- Extract images from PDF
- Fill in a template PDF document
- Fill PDF form
- Fit image to PDF page
- Flatten Markup Annotation
- Flatten PDF form
- How to generate and export certificates
- How do I extract page destinations from bookmarks?
- Highlight fields in PDF
- How to add autosized text to PDF
- How to sign and verify updates to a PDF document
- Import FDF into PDF
- Licensing and .NET Standard
- Merge PDF files in C# .NET
- How to mirror PDF pages and other shapes
- Layout text with MultilineTextShape
- pdfkit5 and .NET Core
- pdfkit5 .NET Standard API
- Read and write meta data from PDF
- Read PDF tags
- How to reduce PDF file size
- Reduce PDF size
- Remove graphics from PDF
- Remove PDF security settings
- Replace field with image
- Resize PDF pages
- Rotate a PDF page
- How to scale content of PDF
- Search text in PDF
- PDF Viewer Preferences
- Create a custom signature handler to sign and verify PDF documents
- Split PDF pages in C# and VB.NET
- Tagged PDF
- TIFF to PDF C#
- Translate PDF page content
- Use multiple licenses
- Use TrueType font collections
- Write Document to HttpResponse
- Use pdfkit5 with a Xamarin.Forms app
- pdfkit5 and Xamarin
Verify a custom digital PDF signature
In the article about create a custom digital PDF signature we explained how to create custom signature handlers. In this article we are going to explain how to verify them using PDFKit.NET.
Verification
If you sign a document with a custom signature, following the code in the article that explains how to create a custom digital signature, and open it in Adobe reader, you will see the following message when you click on the signature.
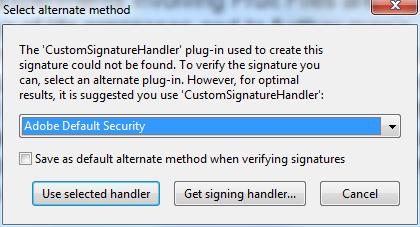
This is to be expected, because Adobe does not know about our custom signature. If you want it to be able to deal with this, you will need to write your own plug-in for Adobe Reader.
This article is not about creating such an Adobe Reader plug-in, but about verifying a custom signature programmatically with PDFKit.NET. As we have seen in the previously mentioned article PDFKit.NET allows you to a define custom signature handler. In this handler you can override the Sign method to provide your own signature, and you can override the Verify method to verify it. It did not however show you how the Verify code will get triggered in PDFKit.NET. This article will show you this.
Please note that the code below has been based on the customSignVerifyAndUpdates sample that is included in the PDFKit.NET distribution.
Usually, verification of “standard” signature fields is very simple in PDFKit.NET. You can call SignatureField.IsSigned to determine whether a signature field has been signed, and a call to SignatureField.Verify() will tell you whether the signature is valid.
When you have fields with custom signatures, this is not enough however, because the standard signature handlers in PDFKit.NET also do not know how to deal with these. In that case, you will need to pass a custom handler to the Verify method, like shown below:
foreach (Field field in document.Fields)
{
// is this a signature field?
SignatureField sigField = field as SignatureField;
if (null != sigField)
{
Console.WriteLine("Field '{0}'", sigField.FullName);
// has it been signed?
if (sigField.IsSigned)
{
// verify, based on our own handler. Note that if you do not pass
// the factory, the default handler will throw an exception
// indicating that it does not support signature type:
// "CustomSignatureHandler / revision 1".
bool verified = sigField.Verify(new CustomSignatureHandlerFactory(sigField.SignedName));
Console.WriteLine(" -- {0}", verified ? "Verified" : "Not verified");
if (verified)
{
// has the document been modified after signing?
bool modified = sigField.DocumentModifiedAfterSigning;
Console.WriteLine(" -- {0}",
modified ? "Modified after signing" : "Not modified after signing");
}
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(" -- Not signed", sigField.FullName);
}
}
}
For Each field As Field In document.Fields
' is this a signature field?
Dim sigField As SignatureField = TryCast(field, SignatureField)
If sigField IsNot Nothing Then
Console.WriteLine("Field '{0}'", sigField.FullName)
' has it been signed?
If sigField.IsSigned Then
' verify, based on our own handler. Note that if you do not pass
' the factory, the default handler will throw an exception
' indicating that it does not support signature type:
' "CustomSignatureHandler / revision 1".
Dim verified As Boolean = sigField.Verify(New CustomSignatureHandlerFactory(sigField.SignedName))
Console.WriteLine(" -- {0}", If(verified, "Verified", "Not verified"))
If verified Then
' has the document been modified after signing?
Dim modified As Boolean = sigField.DocumentModifiedAfterSigning
Console.WriteLine(" -- {0}", If(modified, "Modified after signing", "Not modified after signing"))
End If
Else
Console.WriteLine(" -- Not signed", sigField.FullName)
End If
End If
Next
The custom signature handler factory however, should not just return the custom handler that we have defined. It should not only deal with custom signatures, but it must also work for ‘ordinary’ ones. This means that the factory should inspect the filter and revision of the signature field and return a handler that is appropriate for that particular field. The code below shows this. It only returns our custom handler when the filter and revision are right, otherwise it returns a standard handler.
private class CustomSignatureHandlerFactory : ISignatureHandlerFactory
{
public CustomSignatureHandlerFactory(string name)
{
_name = name;
}
#region ISignatureHandlerFactory Members
public SignatureHandler Create(string filter, int revision, string subFilter)
{
if (filter == "CustomSignatureHandler" && revision == 1)
{
return new CustomSignatureHandler(_name);
}
return (new StandardSignatureHandlerFactory()).Create(filter, revision, subFilter);
}
#endregion
private string _name;
}
Private Class CustomSignatureHandlerFactory
Implements ISignatureHandlerFactory
Public Sub New(name As String)
_name = name
End Sub
#Region "ISignatureHandlerFactory Members"
Public Function Create(filter As String, revision As Integer, subFilter As String) As SignatureHandler
If filter = "CustomSignatureHandler" AndAlso revision = 1 Then
Return New CustomSignatureHandler(_name)
End If
Return (New StandardSignatureHandlerFactory()).Create(filter, revision, subFilter)
End Function
#End Region
Private _name As String
End Class
When SignatureField.Verify(new CustomSignatureHandlerFactory(sigField.SignedName)) gets called for a field that has been signed with a custom signature, our own custom signature handler will be used to verify the field. This means that the Verify method of the custom handler will be invoked, and that the result will be passed to SignatureField.Verify(…).
Please note that the result of SignatureField.Verify(…) also determines whether a document has been tampered with. The verify method should return false when the signature digest no longer matches the document.
This must not be confused with a call to SignatureField.DocumentModifiedAfterSigning. The latter does not indicate whether a document has been tampered with. SignatureField.DocumentModifiedAfterSigning indicates whether a document has been been updated in a regular way after signing, by appending an update. If such an update is appended, this will not invalidate the signature for the earlier revision of the document, but PDF readers will signal this, so that it is clear to users that an earlier version was signed, an not the current version.
Note also that if a document has been updated after signing, that PDFKit.NET allows you to obtain the earlier signed version via the SignatureField.SignedUpdate property. So, if a signature is valid – i.e. Verify() returns true -, it is always possible to inspect the version that was signed.